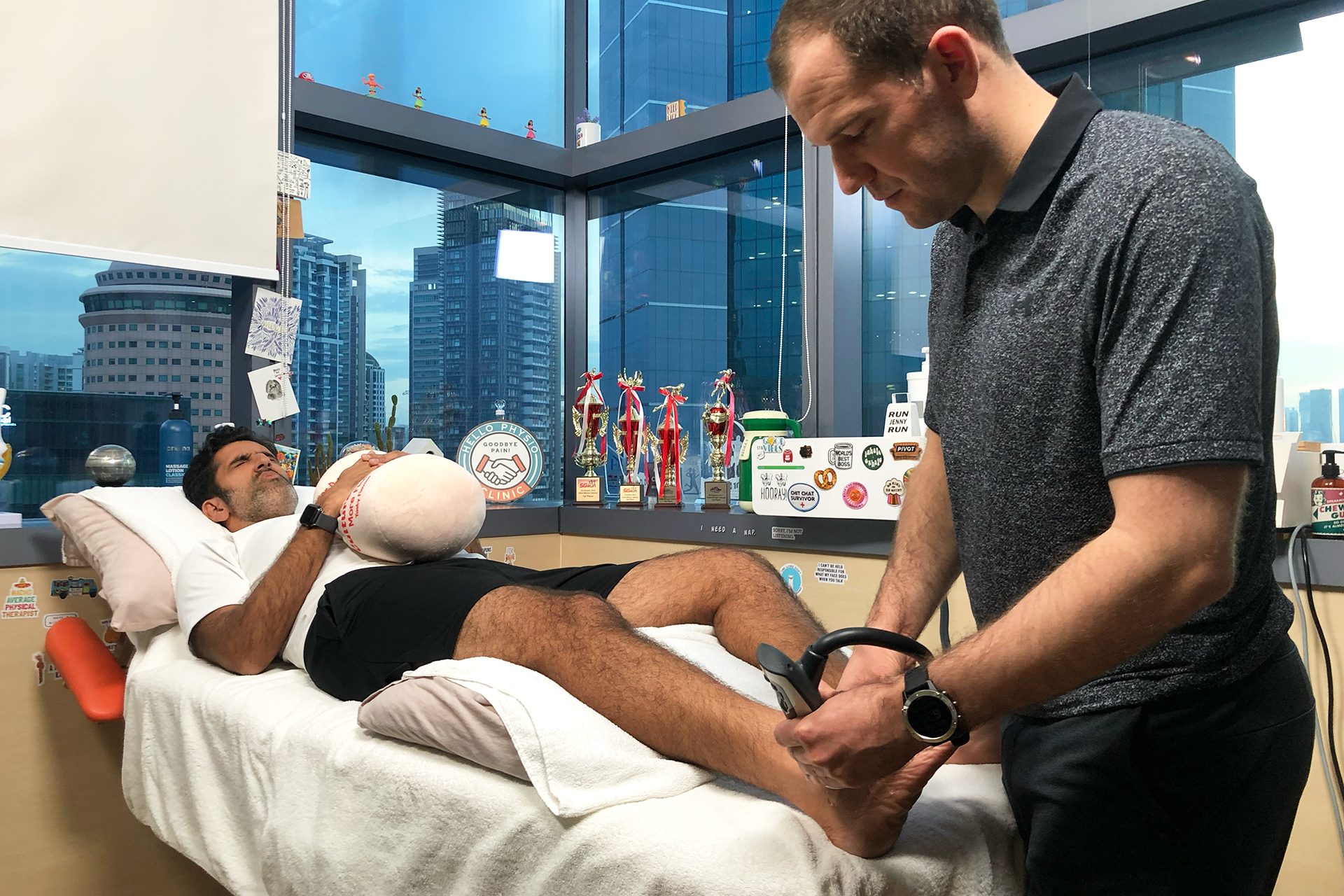
Ankle Sprain Treatment
Diverse conservative treatments are available for managing sprained ankles beyond the traditional recommendations, such as short-term immobilization, complete immobilization, applying ice packs, and using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
At HelloPhysio, we approach ankle sprains from a broader context. Our skilled multidisciplinary team assesses every contributing factor, from lifestyle and exercise habits to recovery processes. We offer manual therapy, supportive adjunctive therapies, and personalized prescriptive exercises designed to alleviate pain quickly and safely and restore movement.
Our treatment approaches synergistically enhance mobility and strength, minimizing stress on the healing ligaments to reduce the likelihood of re-injury risk. This integrated strategy ensures a more effective and sustainable recovery process.
Bringing the deep heat generated by INDIBA® Activ improves blood circulation; this enhanced blood flow carries essential nutrients and oxygen to the injured area, optimizing the environment for tissue repair stimulated by Shockwave Therapy. Ultrasound shockwaves create micro-trauma within the injured tissues, triggering the body’s natural healing response to increase blood flow and promote the growth of new, healthy tissue.
Combined with prescriptive exercises, our treatment approach to sprained ankles minimizes stress on the healing ligaments, thereby providing lasting pain relief and reducing the likelihood of re-injury.
Book an Appointment
Exploring the Mechanism of an Ankle Sprain
An ankle sprain ranks the foremost musculoskeletal injury impacting the lower limb among physically active people. This condition arises from the stretching, partial tearing or complete rupture of one or more ligaments within the ankle joint due to an involuntary twisting action that surpasses the joint’s typical range of motion.
An ankle sprain’s mechanism of injury involves a triad of movements where the foot turns inward and downward while also rolling outwards, which leads to the degradation of the external lateral ligament and frequently affects the anterior peroneal tendons.
There are three main types of ankle sprain patterns: lateral, syndesmotic, and medial. Most ankle sprains happen to the lateral ligaments because it’s less able to withstand force, making them more prone to injury. The lateral ligament group in the ankle includes the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL), the calcaneofibular ligament (CFL), and the posterior talofibular ligament (PTFL).
The ATFL is the most prone to injury, and its damage often leads to anteroposterior instability, while CFL damage can cause instability during inversion movements.
In exceptional circumstances, the anterior ligament may be torn, with associated capsular damage and rupture of the peroneal tendons. The deltoid ligament may be damaged by traumatic eversion. However, this type of sprain occurs only rarely. The possibility of associated injuries, such as distal or proximal fracture of the fibula and the talus, should be considered.
Under exceptional conditions, the anterior ligament might suffer a tear, accompanied by capsular damage and rupture of the peroneal tendons. Traumatic eversion can lead to injury of the deltoid ligament, though such sprains are infrequent. Physiotherapists also evaluate for potential concurrent injuries, including fractures of the fibula and the talus, whether closer to the knee (proximal) or near the ankle (distal).
Additionally, excessive upward bending of the foot may injure the syndesmotic ligaments. Beyond ligaments, this condition can also impact other anatomical structures, including bones, muscles, tendons, nerves and blood vessels.
The clinical signs of a sprained ankle encompass difficulty walking or moving the joint, a sharp or tearing feeling, increased pain with movement, discolouration, and swift onset of bruising. The severity of the sprain dictates the intensity of these symptoms.
Rehabilitation and restoration of function post-sprain can range from non-surgical to surgical interventions. Non-surgical (conservative) treatment is typically recommended for Grade I and II sprains. In contrast, Grade III sprains often require surgical intervention, though occasionally, a conservative approach may also suffice for these more severe sprains.
Acute Ankle Sprains in Athletes
Acute ankle sprains are more prevalent during indoor sports like volleyball, basketball, and dance, as well as outdoor activities like running, football, or rugby.
Most people, whether athletes or not, will experience an ankle sprain at some point in their lives. This type of injury occurs more commonly in women than in men. It is also more prevalent in children than adolescents and adults, highlighting the role of developing coordination patterns and neuromuscular control in children.
A small percentage of acute ankle sprains are accompanied by an ankle or foot fracture, highlighting that these injuries predominantly involve soft tissues. This insight supports our sprained ankle treatment, incorporating INDIBA® radiofrequency, Shockwave Therapy, and specifically prescribed exercises to enhance strength and mobility.
Connect with Physiotherapists and Rehabilitation Team
Our senior physiotherapists and rehabilitation team, extensively trained in musculoskeletal dysfunctions, orthopedic disorders, acute conditions and sports injuries, are experienced clinical health professionals who actively guide your rehabilitation to help you achieve your performance goals.
To learn more about our multimodality sprained ankle treatment approach, please contact or call the clinic to speak with or meet our team.