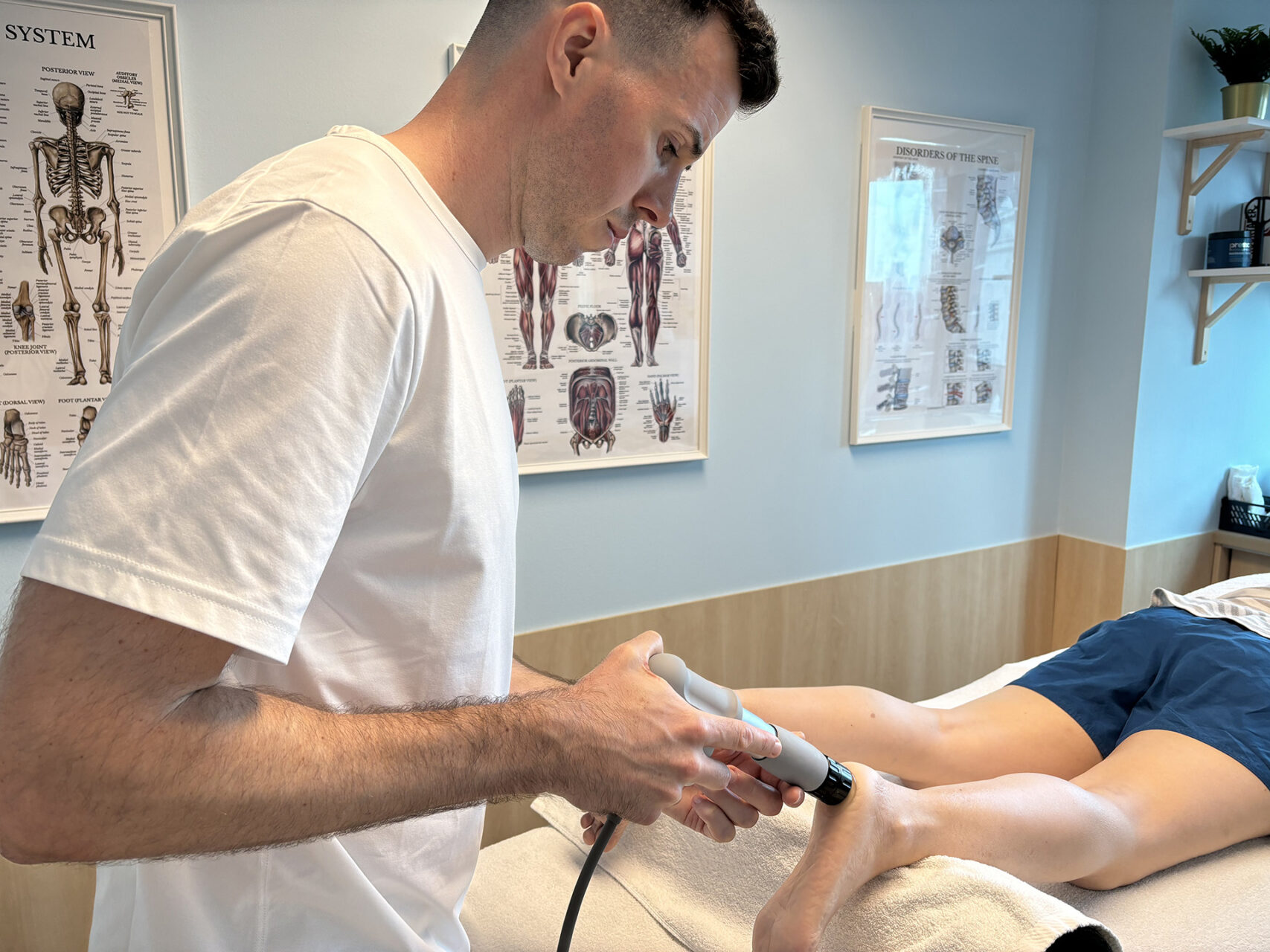
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
What Is Insertional Achilles Tendonitis?
Insertional Achilles tendonitis is a painful condition that affects the area where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel bone. Unlike mid-portion tendonitis, which occurs higher up the tendon, insertional issues are often aggravated by compression during ankle movements, such as dorsiflexion.
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body, connecting the calf muscles, specifically the gastrocnemius and soleus, to the calcaneus, or heel bone. Insertional Achilles tendonitis refers to inflammation, irritation, or degeneration at the Achilles tendon insertion, specifically on the Achilles tendon, where it attaches to the back of the heel.
Insertional Achilles tendonitis can affect athletes and anyone exposed to repetitive strain or biomechanical inefficiencies. While the pain can be persistent and disruptive, if you have ongoing heel pain or discomfort at the back of your heel, you should seek professional help. The good news is that most cases respond well to targeted exercises and structured physical therapy for Achilles tendonitis.
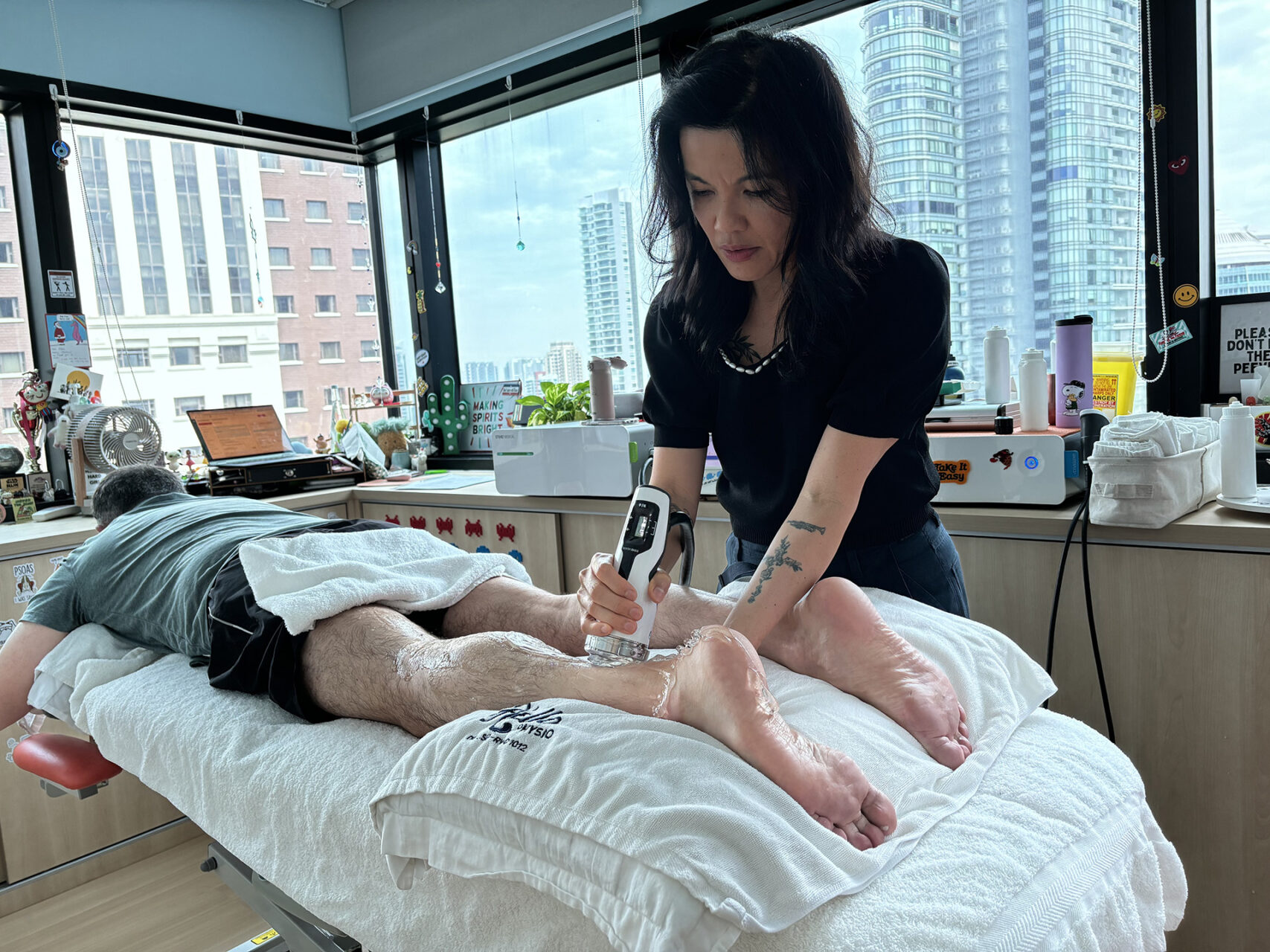
What Causes Achilles Tendon Insertion Pain?
Insertional Achilles tendonitis pain is commonly caused by overuse, excessive compression at the tendon’s insertion point, and faulty movement patterns that overload the heel. Achilles tendonitis occurs in runners and in individuals who engage in physical activity involving uphill movement, stairs, or high-impact landings.
is frequently observed.
Mechanical overload, such as sudden increases in activity or repetitive strain from running or jumping, is a common cause of injury. Biomechanical abnormalities, such as flat feet or high arches, can alter the distribution of force across the tendon, increasing the likelihood of insertional Achilles tendonitis. Systemic factors, such as age-related changes, certain health conditions, and even specific medications, may also contribute to the development of tendinopathy.
It is important to recognize that the condition of the foot, leg muscles and tendons all play a role in the health of the Achilles tendon. By being aware of these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps, such as proper training, stretching, and strengthening exercises, to reduce the risk of developing Achilles tendinopathy and maintain tendon health.

Recognizing the Symptoms
The hallmark symptom of insertional Achilles tendonitis is a deep, localized pain at the back of your heel, specifically at the Achilles tendon insertion and on the Achilles. This pain is often most noticeable when sitting, standing, or walking uphill.
Many people report tail-end morning stiffness and sharp pain in the tailbone when sitting, although these symptoms may overlap with those of other conditions. In more severe cases, the Achilles tendon is thickened at its insertion, with tenderness to palpation, indicating chronicity.
Pain often builds gradually, but once established, it can significantly affect your ability to walk, climb stairs or engage in physical activity. If you have persistent heel discomfort, especially if it’s not improving with rest, you should consider a physiotherapy assessment.
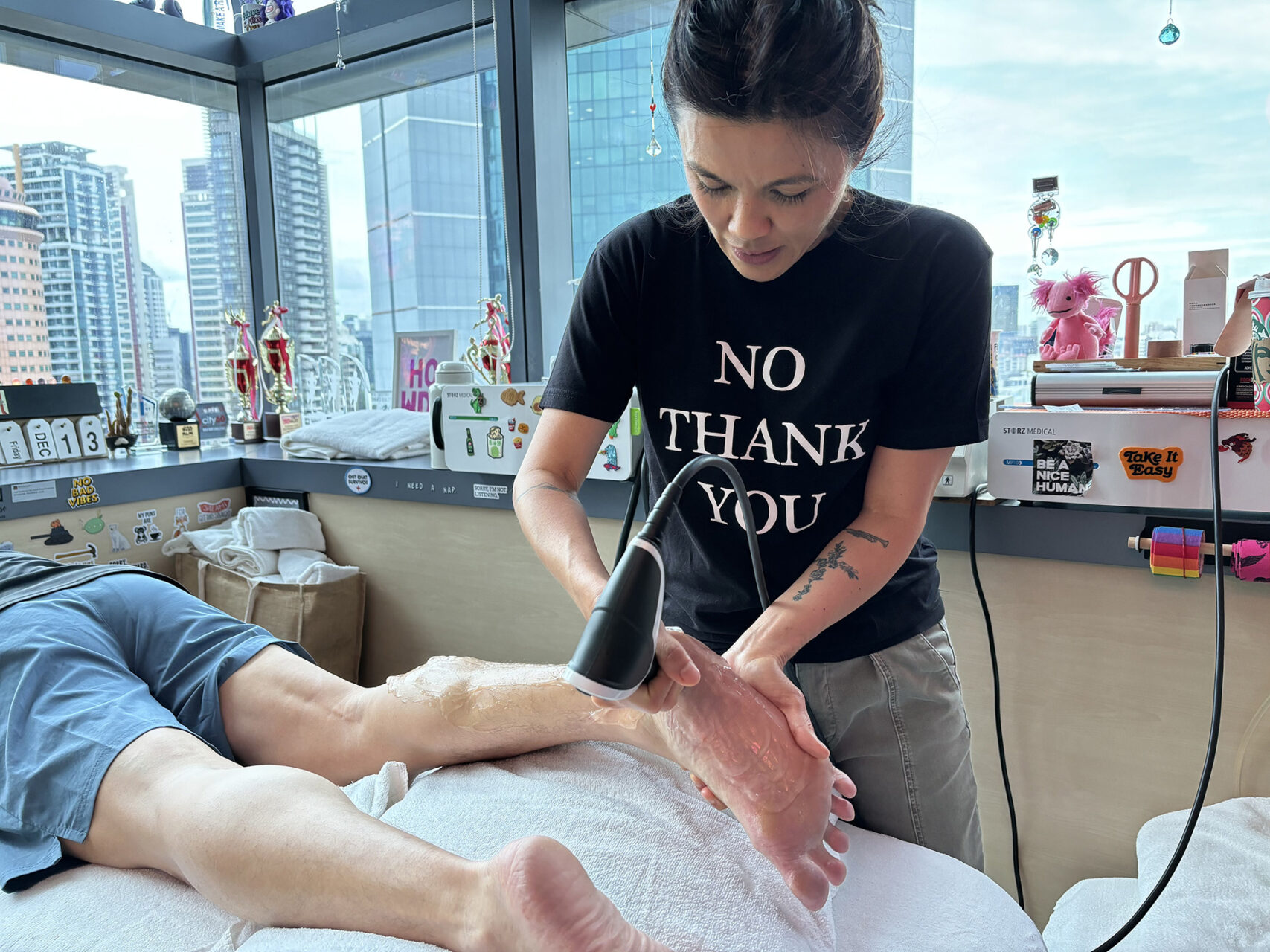
Diagnosing Insertional Achilles Tendonitis
A clinical diagnosis usually begins with a detailed physical exam and review of your activity history for insertional Achilles tendonitis. Your physiotherapist will assess the range of motion in your feet and ankles, calf strength, gait, and postural alignment, with a particular focus on the Achilles tendon insertion. Imaging studies, such as an ultrasound, can help visualize tendon thickening or degeneration, while an MRI may be recommended if symptoms are atypical or persistent.
Understanding the root cause of the condition, whether it’s biomechanical, degenerative or related to load management, is crucial for prescribing the proper treatment for insertional Achilles tendonitis.
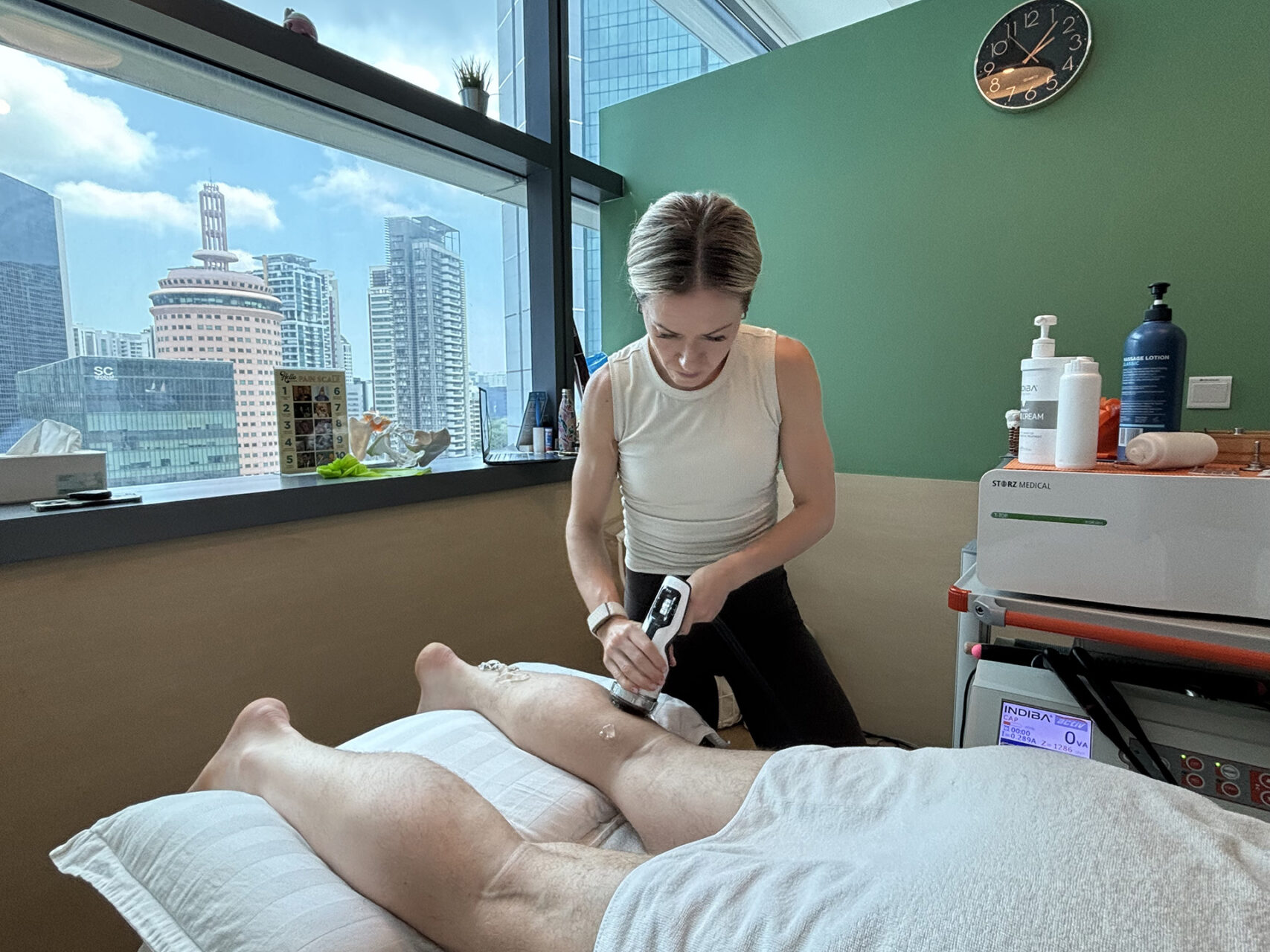
Physiotherapy and Targeted Exercise
Exercise is the cornerstone of non-surgical treatment for Achilles tendinitis. The aim is to improve tendon structure and function through controlled, progressive loading, with specific exercises prescribed to enhance tendon structure. In the early stages, isometric exercises, where the muscle is activated without changing its length, can help reduce pain and improve load tolerance as a first-line intervention. These are particularly helpful when standard exercises are too uncomfortable.
Simply resting the tendon won’t rebuild its capacity, while overloading it can worsen symptoms such as tendon pain and Achilles tendon pain. The goal is to gradually reintroduce movement and strength through a tailored exercise program that includes strengthening exercises to progressively increase tendon capacity and build resilience without causing flare-ups.
As symptoms improve, patients transition to heavy, slow resistance training, aiming to stimulate tendon remodelling and enhance their ability to store and release energy. Unlike protocols for mid-portion tendonitis, exercises for insertional tendonitis often avoid ankle dorsiflexion to limit compression at the tendon insertion.
These Achilles tendinitis treatment exercises are best prescribed and monitored by a physiotherapist, who can make adjustments based on your pain response and functional goals.
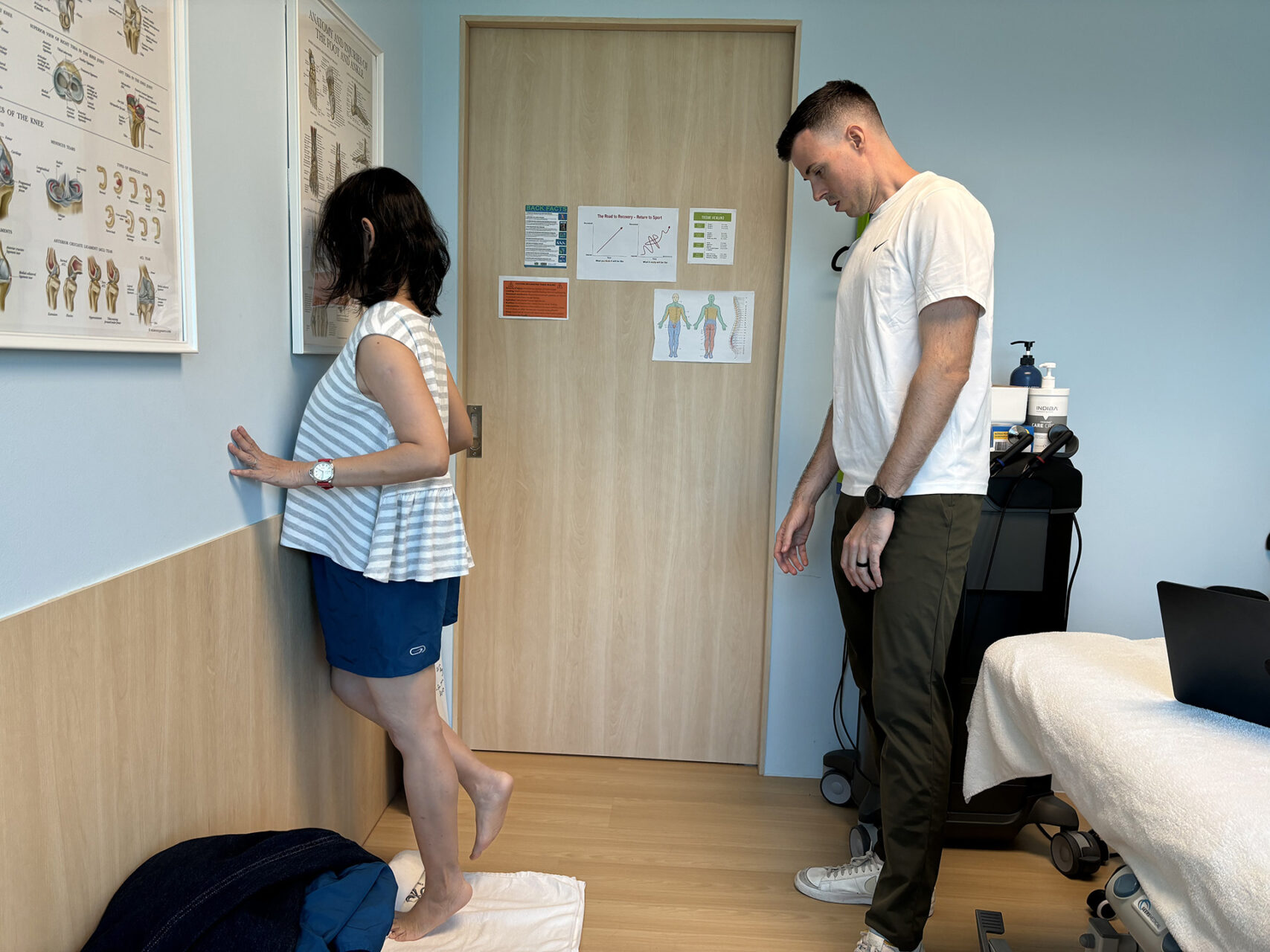

Enhancing Outcomes with Adjunct Therapies
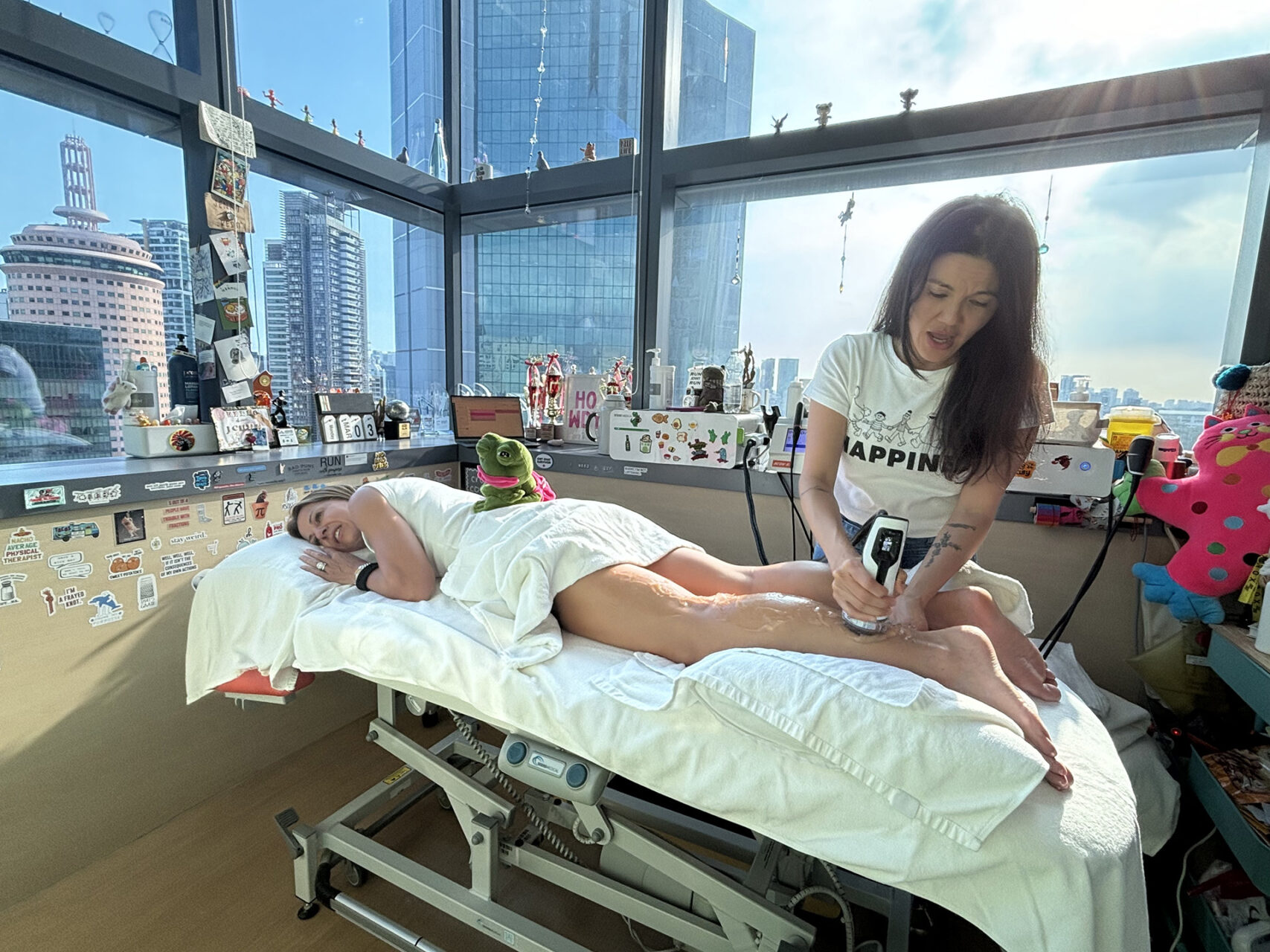
While exercise is essential, adjunctive therapies can support tendon healing, reduce pain, and expedite recovery from Achilles tendonitis, particularly when treatment progress is slow in insertional Achilles tendonitis. Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) is a widely used modality that delivers acoustic waves to the Achilles tendon, promoting circulation and cellular repair to reduce chronic symptoms. For many patients with chronic Achilles tendon insertion pain, Shockwave Therapy for Achilles tendonitis can sufficiently alleviate symptoms to enable consistent exercise participation as a supportive treatment.
At HelloPhysio, we also incorporate INDIBA®, a radiofrequency-based modality that enhances blood flow and supports soft tissue recovery. When used in conjunction with a structured loading plan, these tools can accelerate healing and improve long-term outcomes.
Combined with manual therapy techniques and patient education, these modalities round out a truly individualized rehab program.
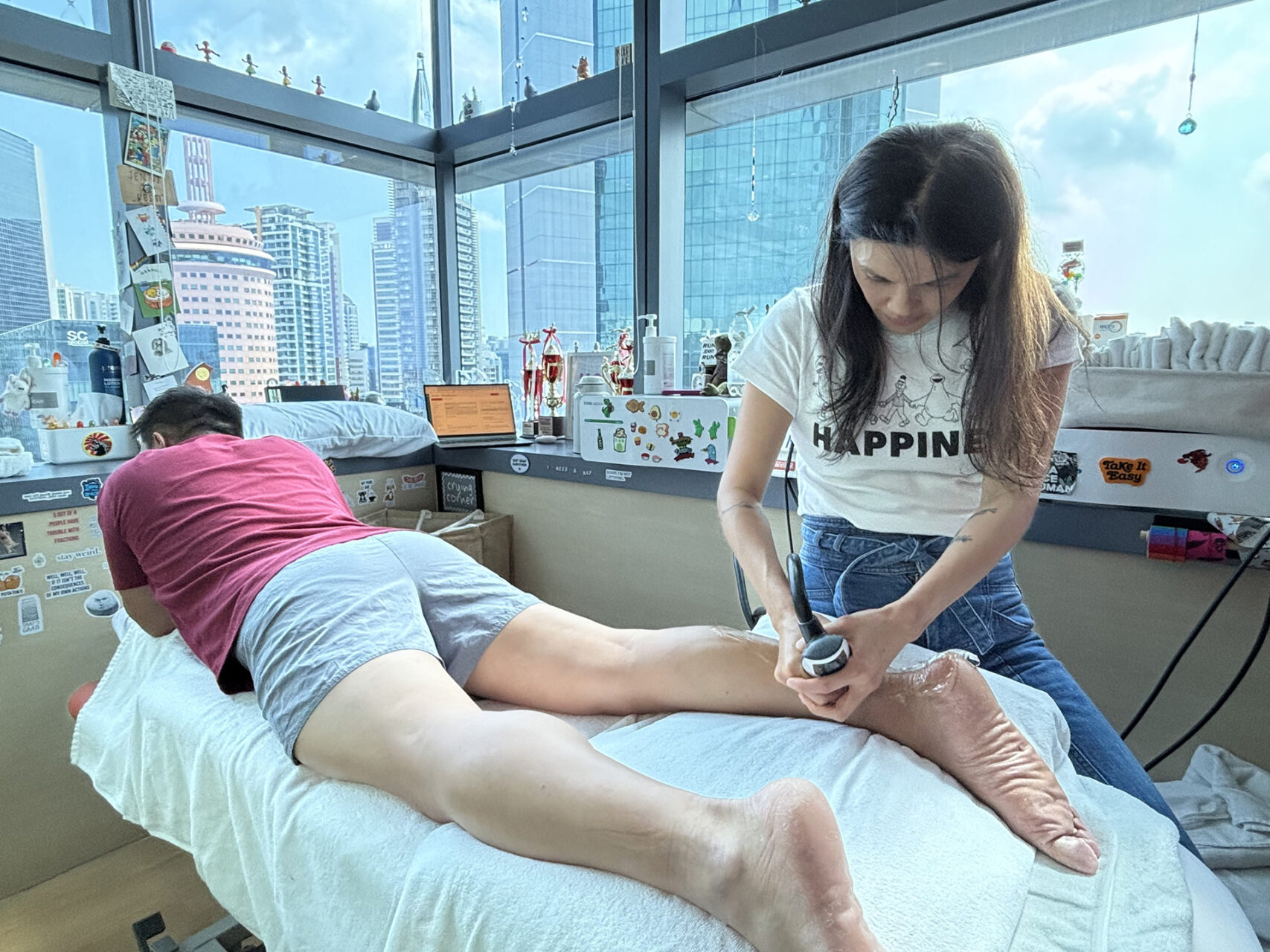

Footwear and Orthotic Support
Proper footwear is essential when managing insertional Achilles tendonitis, particularly for the foot and ankle, as orthotic support can play a significant role. Shoes with a slightly elevated heel can reduce tendon compression and redistribute pressure, thereby alleviating pain in the tendons and Achilles tendon. In some cases, temporary heel lifts may be inserted into the shoe to provide additional cushioning and pressure redistribution.
Chronic or complex cases may benefit from custom orthotics, particularly when faulty foot mechanics contribute to the problem. Taping for insertional Achilles tendonitis may also be used during transitions back to activity, offering added support and confidence in movement.

What If Conservative Care Fails?
Most people respond well to physiotherapy-led treatment. However, when symptoms such as tendon pain, including Achilles tendon pain, persist despite appropriate care, further medical intervention may be considered for refractory cases. Anti-inflammatory medications may provide temporary relief but can also delay tendon healing and are not a long-term solution.
Corticosteroid injections are generally avoided in insertional tendonitis due to the risk of weakening the tendon. If needed, they must be administered with caution and always as a part of a broader rehab strategy, as a last resort.
Surgical options are reserved for more advanced cases and may include debridement of diseased tissue or tendon reattachment. More importantly, postoperative rehabilitation is essential for restoring strength, mobility, and tendon function.
Preventing Recurrence and Promoting Long-Term Recovery
Insertional Achilles tendonitis pain relief isn’t just about calming down inflammation. It’s about restoring the tendon’s ability to handle the demands of your lifestyle or sport and preventing the return of symptoms. Incorporating strengthening exercises is essential for preventing recurrence as a long-term strategy to maintain tendon health, and a gradual return to running or activity, guided by a physiotherapist, helps minimize setbacks.
Understanding how to treat insertional Achilles tendonitis begins with recognizing the importance of early intervention, ongoing care for the prevention of future tendon pain, and respect for your body’s limits. Maintaining ankle and calf mobility, regularly strengthening the posterior chain, and wearing appropriate footwear are all essential components of a comprehensive long-term plan.
Even after symptoms resolve, continuing your home exercises and maintaining a balanced level of activity can help prevent future flare-ups.
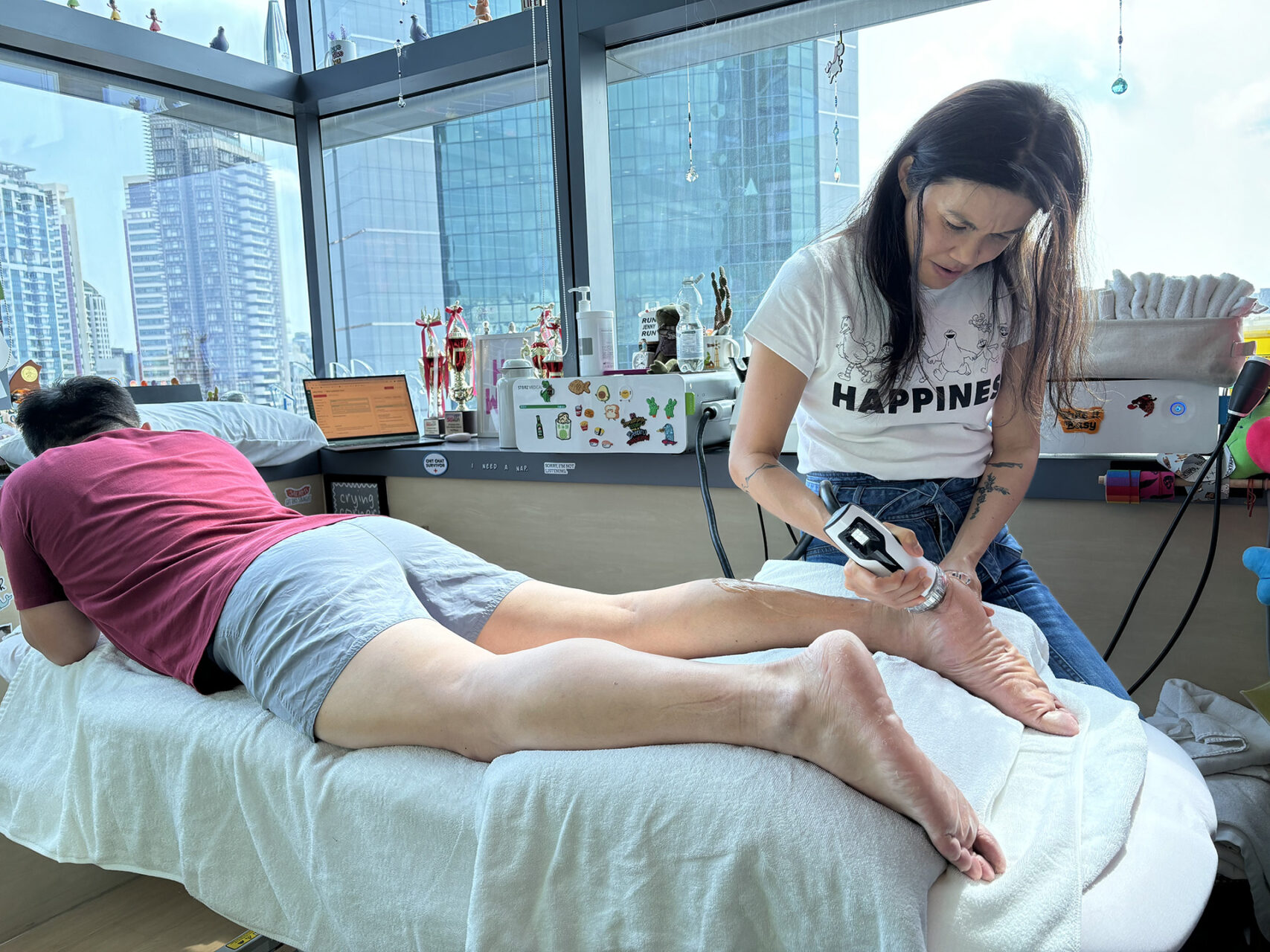

A Collaborative Approach to Healing
At HelloPhysio, we treat insertional Achilles tendonitis with a comprehensive and evidence-based approach to diagnosis and rehabilitation. Our assessment includes a thorough evaluation of the foot and ankle to ensure all contributing factors are addressed.
By combining physiotherapy, taping strategies, adjunct modalities such as Shockwave Therapy and INDIBA, and carefully selected strengthening exercises, we help patients reduce pain, regain function, and return to activities they enjoy. Reach out to the team at HelloPhysio for a personalized consultation for your insertional Achilles tendonitis pain.