|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
That nagging ache at the back of your knee can creep up on you and turn a simple jog or stair climb into a frustrating experience. Posterior knee pain is often associated with swelling, limited leg bending, or underlying conditions such as ligament injuries. Back of knee pain isn’t just an annoyance; it’s a sign that something’s off in that complex area where muscles, tendons and ligaments meet.
Whether it’s pain in the back of the knee when bending or a sharp twinge when straightening, understanding is the first step to getting back to smooth movement. At HelloPhysio, we often see this common issue, and the good news is that physiotherapy can not only ease the discomfort but also rebuild strength and prevent recurrence.
Introduction to Knee Pain
Knee pain is one of the most common complaints among people of all ages, ranging from athletes to office workers. The knee joint is a complex structure composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments and tendons that all work together to support movement and bear weight. Due to this complexity, the knee is particularly susceptible to a wide range of injuries and conditions. Understanding the various causes and types of knee pain is the first step toward finding relief and protecting your knee joint in the long term.

Common Causes of Back of Knee Pain
Muscle and Tendon Strain
Leg muscles are one of the most common reasons for pain at the back of the knee when bending your knee or stretching. This is often a sign of a strained hamstring or calf.
A calf strain, which affects the gastrocnemius or soleus muscle in the lower leg, can cause pain, swelling, bruising and difficulty standing on tiptoes at the back of the knee. These muscle groups run across the joint and are heavily involved in sports, running, and even daily activities like climbing stairs.
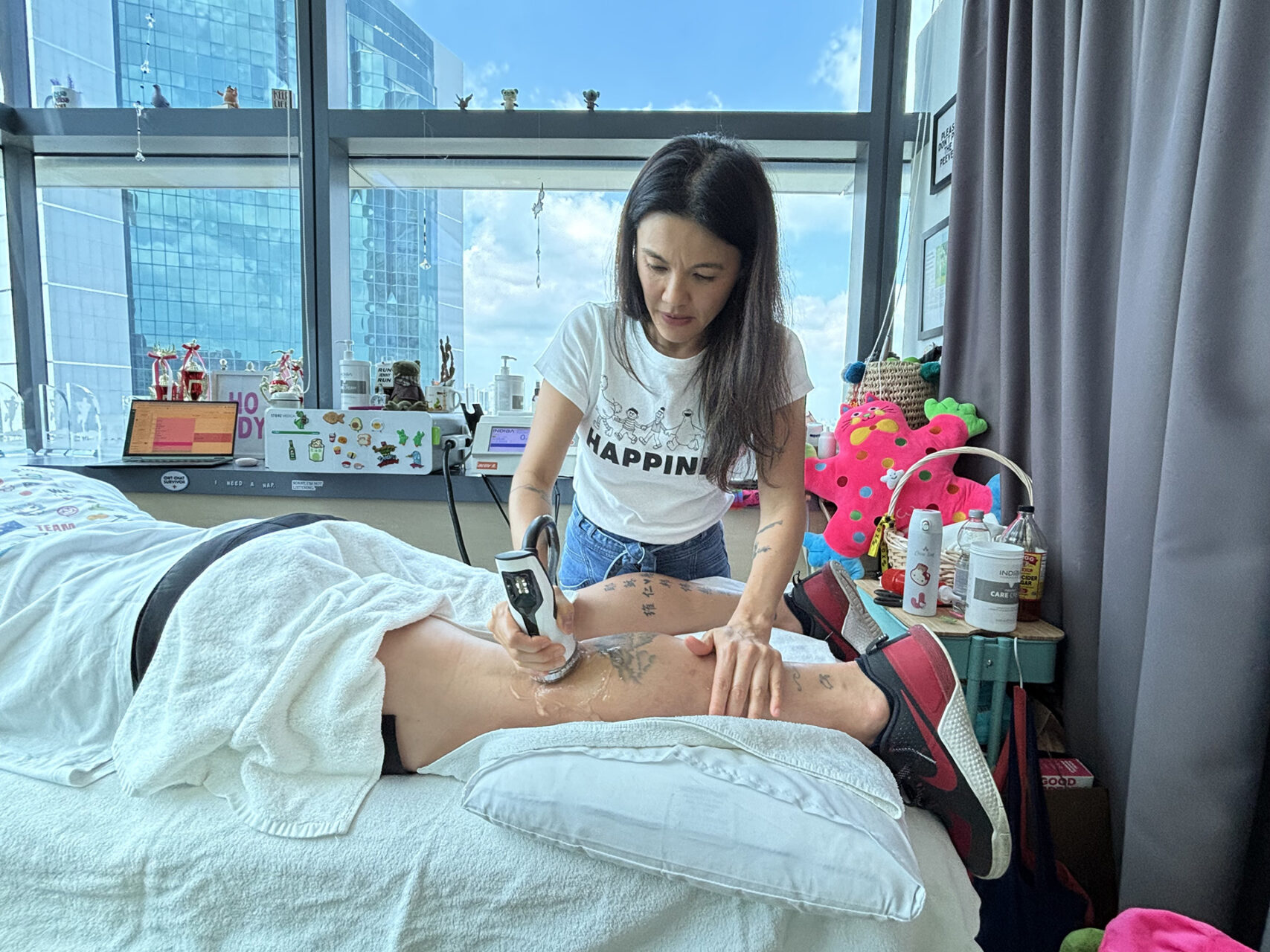
Overuse or sudden overload can cause tiny tears, microtears in the muscle or tendon fibers, leading to pain, swelling and tightness. Physiotherapy focuses on restoring flexibility and building strength, utilising modalities like INDIBA® to reduce inflammation and accelerate tissue repair.
Baker’s Cyst
A Baker’s Cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled swelling that forms at the back of the knee, usually as a secondary effect of another problem like arthritis or a meniscus tear. While Baker’s cysts themselves are generally harmless, they can cause a noticeable bulge and discomfort, especially when your knee is bent.
Treatment often involves managing the underlying condition, reducing fluid buildup, and using manual therapy alongside adjuncts, such as Shockwave Therapy, to relieve stiffness and promote circulation. Baker’s cysts can sometimes resolve on their own, but a painful cyst or large cyst may need drainage or other procedures.
Meniscus Tear
The meniscus sits between the thigh bone (femur) and the shin bone, helping to absorb shock and stabilize the joint. A twisting motion of the knee, mainly when the thigh bone rotates on the lower leg, is a common cause of a torn meniscus. This injury can sometimes cause pain in the back of the knee when bending the knee joints. Symptoms may include locking, catching or swelling.
Physiotherapists often design tailored rehab plans that combine strengthening exercises with gentle mobilizations to restore stability for the meniscus. In cases where surgery is required, post-operative care focuses on safe, progressive loading and tissue healing.
Tendonitis
Inflammation of the tendons, particularly those connecting the hamstring or calf muscles to the knee, can cause discomfort in the back of the joint. Tendonitis often develops from repetitive strain, poor biomechanics or sudden increases in activity. Biceps femoris tendonitis is a common cause of pain at the back of the knee, particularly in athletes, resulting from strain or injury to the biceps femoris tendon, the two-headed muscle on the outside of the back of the thigh. The tendons surrounding the knee joint play a crucial role in movement and stability, and their involvement in overuse or injury can significantly contribute to knee pain.
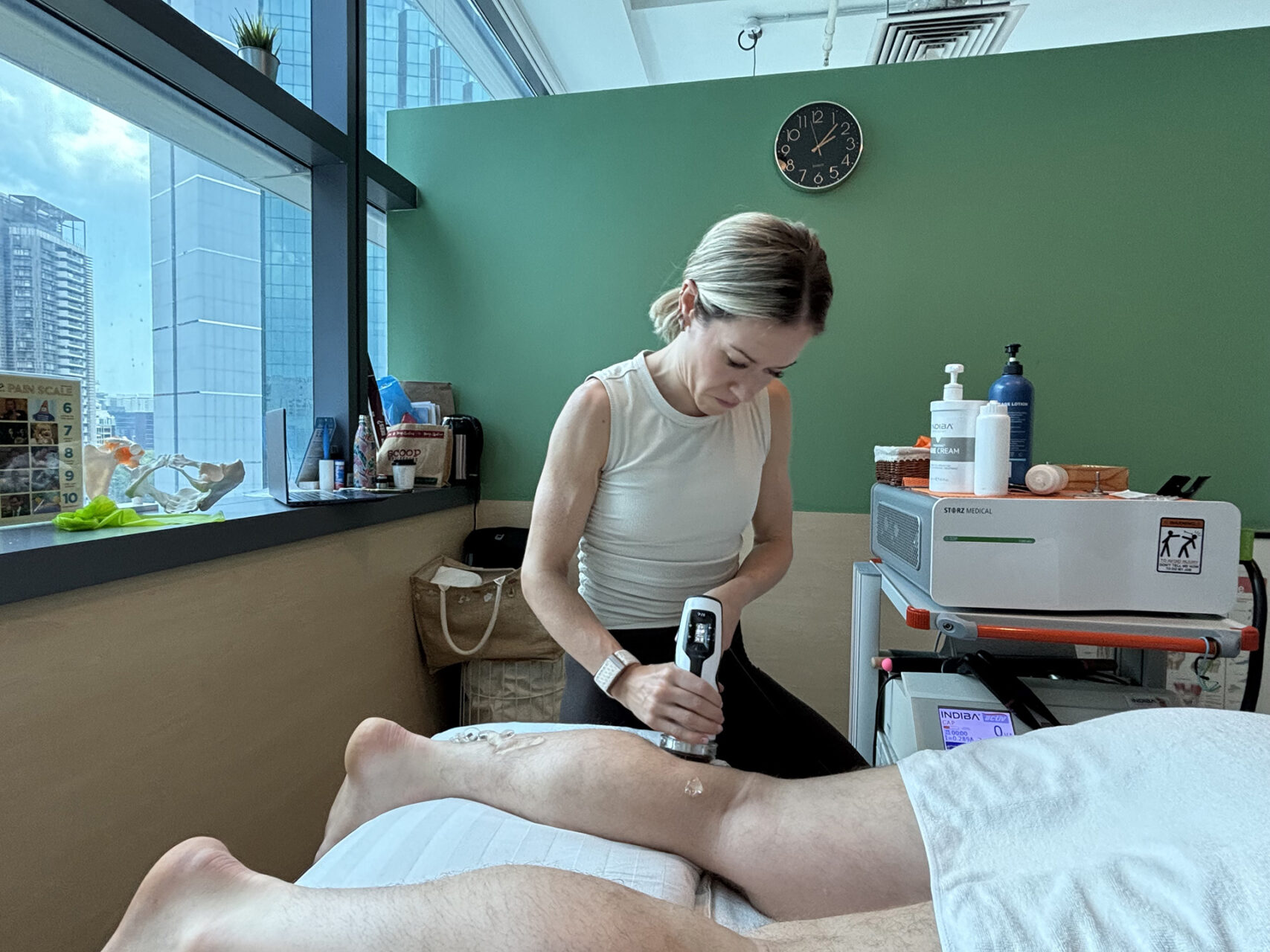
Physiotherapy treatments include targeted eccentric exercises, dry needling to release tension and Shockwave Therapy to stimulate tendon healing.
More Serious Causes of Back of Knee Pain
Ligament Tears
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is another major ligament that can be injured, often during sports. The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) sits at the back of the knee and is vulnerable to injury during trauma such as falls or car accidents. An ACL injury typically results from sudden stops or changes in direction, while a PCL injury can occur from direct blows to the knee or hyperextension.
Management may involve bracing and rehabilitation in less severe tears or surgical repair for complete ruptures. If more than one ligament is torn in a knee injury, surgery may be required to restore knee stability. Physiotherapy after injury or surgery is vital, addressing both strength and functional stability to prevent re-injury.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
While less common, pain in the back of the knee when straightening the leg can be a sign of a more serious condition. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) often presents with leg swelling as a key symptom. Blood clots forming in the deep veins can cause leg pain and swelling, along with redness and warmth in the affected leg. If a blood clot travels to the lungs, it can result in a life-threatening pulmonary embolism. DVT is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention.
Tumors or Infections
Rarely, growths or infections can cause persistent pain in the area behind the knee. Autoimmune conditions, such as psoriatic arthritis, can also cause pain and swelling in the knee and other joints, sometimes accompanied by skin symptoms. These cases highlight the importance of proper diagnosis.
Physiotherapists at HelloPhysio work closely with medical specialists to ensure safe care, only intervening when serious causes have been ruled out or treated.
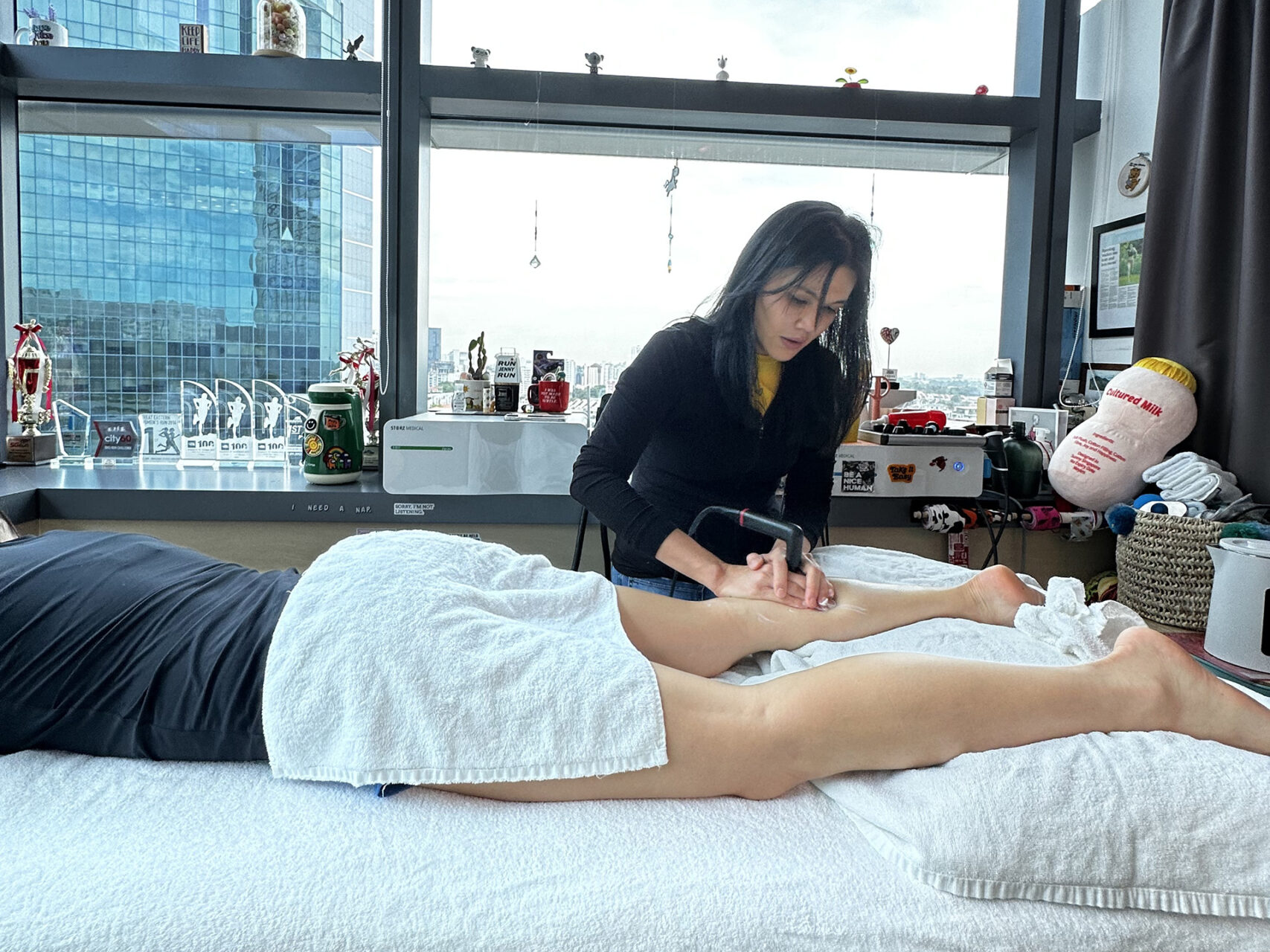

Symptoms and Diagnosis
Knee pain can present in various ways, depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include aching, sharp pain, swelling, stiffness and difficulty moving or bearing weight on the affected knee. Some people may notice redness, warmth, or a constant feeling of instability in the joint.
To diagnose the source of knee pain and relieve it effectively, healthcare professionals begin with a thorough physical examination and review of the medical history. Imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans may be used to get a closer look at the knee joint and surrounding tissues. In some cases, blood tests or joint fluid analysis may be used to rule out infections or autoimmune conditions.
Complications and Risks of Knee Pain
Knee pain can become chronic, making everyday activities increasingly complicated and increasing the risk of falls or further injury. In some cases, knee pain can be a warning sign of more serious health issues, such as rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the joints, or deep vein thrombosis, a blood clot in a deep vein that can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
If you experience severe pain, swelling, redness, or other concerning symptoms, seek medical attention right away. Early intervention can help relieve pain, address the underlying cause and prevent complications that can impact your long-term health and mobility.
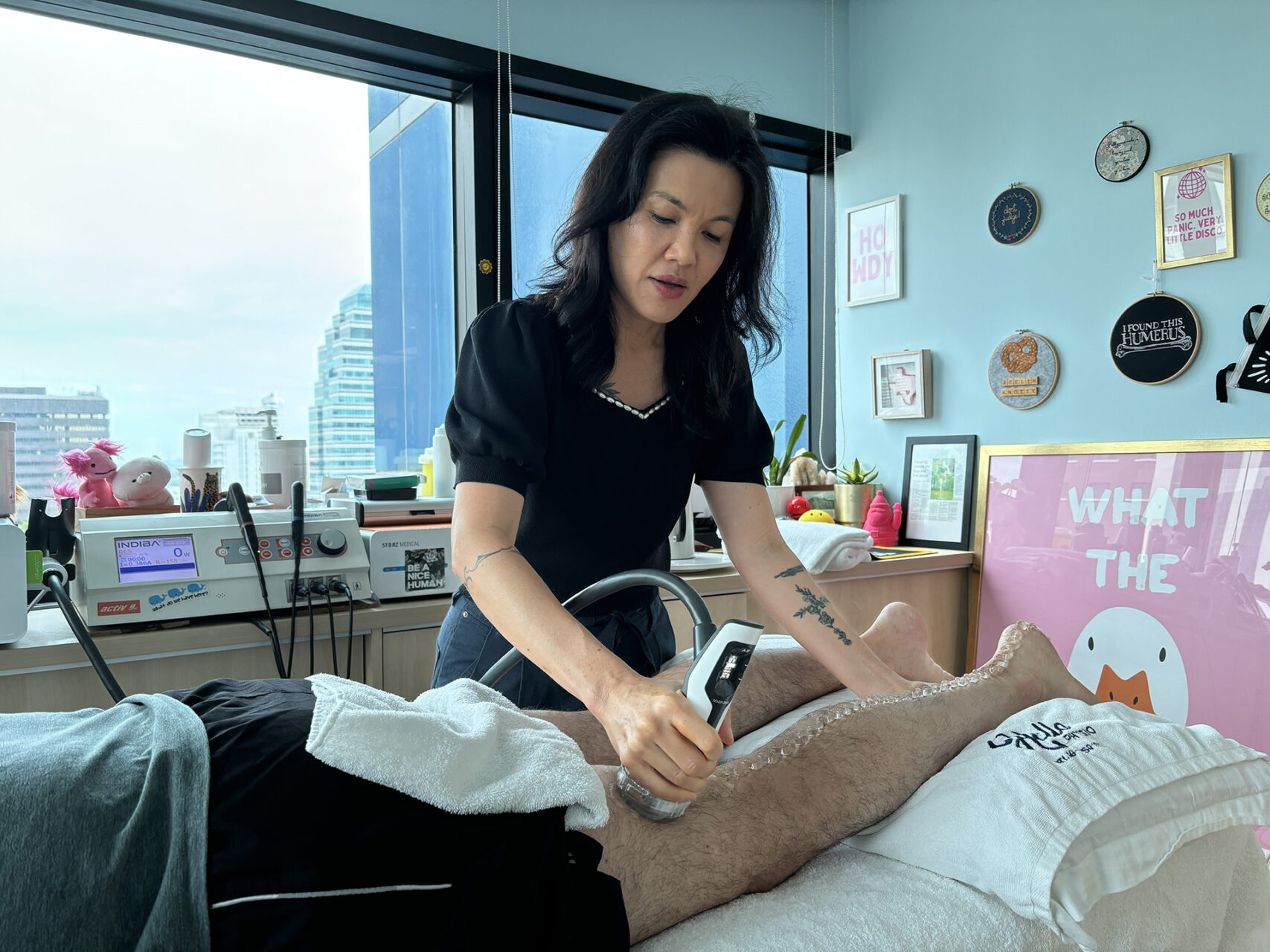

How Physiotherapy Helps with Back of Knee Pain
Effective management of back-of-knee pain begins with a proper diagnosis. A thorough assessment at HelloPhysio includes examining gait, mobility and muscle balance, alongside reviewing lifestyle factors such as footwear, training habits and work demands. Physiotherapists assess pain signals from muscles, ligaments and joint structures to determine the source and severity of your symptoms and tailor knee pain treatment plans accordingly. This holistic approach ensures that both the symptoms and the root causes of your knee pain are addressed.
For example, a runner with back-of-knee pain when bending may need adjustments to running technique, footwear, or hamstring and glute strengthening. Office workers experiencing stiffness from prolonged sitting in Singapore’s CBD may benefit from mobility exercises, postural correction, and targeted stretches.
Conservative management often involves knee rest and the use of an elastic bandage to provide compression, reduce swelling, and stabilise the joint. Physiotherapy aims to treat pain and restore function through a combination of the prior strategies and individualised exercise programs.
Adjunctive modalities are seamlessly integrated into treatment:
- INDIBA Activ uses radiofrequency energy to accelerate healing, reduce inflammation and improve circulation. It is particularly effective for tendonitis or muscle strain.
- Shockwave Therapy delivers acoustic waves that stimulate tissue regeneration and break down scar tissue, often used for chronic tendon or meniscus-related pain.
- Dry Needling targets trigger points in tight muscles, releasing tension and improving flexibility in the surrounding area, including the knee.
Along with manual therapy and prescriptive exercises, these tools form a comprehensive plan that not only relieves pain but also strengthens and stabilises the joint for long-term resilience.
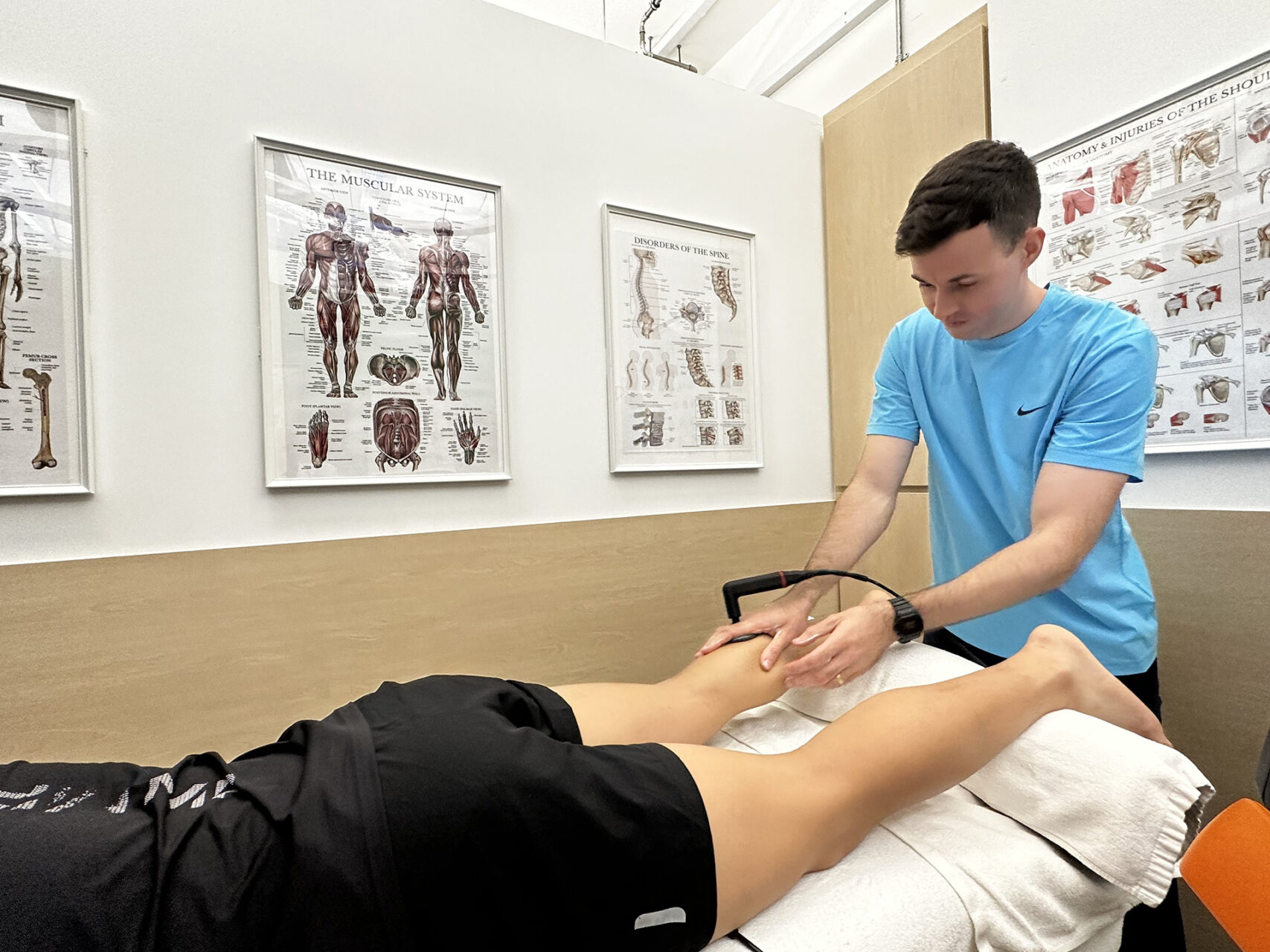
What Patients Experience
Many patients experience back-of-knee pain as a sharp pull, often after prolonged periods of sitting or standing. Some also report their knee feels sore after activity, which can be a sign of underlying issues. Others report pain in the back of the knee when bending, especially during squats or lunges.
Athletes may experience sudden pain in the back of the knee during sprints or pivoting, while older individuals may struggle with stiffness due to degenerative changes. These types of discomfort, including knee soreness and posterior knee pain, highlight the importance of proper assessment.
HelloPhysio’s approach is to match each treatment plan to the patient’s lifestyle. For a runner preparing for the Standard Chartered Singapore Marathon, for example, rehab may include progressive loading on antigravity treadmills, such as the LightSpeed Lift, which allows for the safe reintroduction of running mechanics while reducing impact. For someone dealing with pain after a desk-bound day, the focus may be on ergonomic advice, mobility drills and targeted stretches.
Prevention
Prevention is key to physiotherapy at HelloPhysio. Strengthening surrounding muscles, correcting movement patterns, and maintaining flexibility are all key strategies for improving overall performance. Clinical Pilates is often recommended to retrain alignment and ensure efficient movement across the lower limbs and core.
Footwear assessments, sport-specific drills and progressive return-to-play protocols ensure that whether you are a weekend footballer at Bishan Park or a dancer rehearsing in Bugis, you can return to activity with confidence and a lower risk of reinjury.
Get Help for Your Back of Knee Pain
Back-of-knee pain should not be ignored. Early assessment by a physiotherapist can help prevent minor strains from developing into chronic injuries. If you suspect something serious, such as a ligament tear or DVT, immediate medical attention is essential before rehabilitation begins.
With evidence-based care and advanced treatments like INDIBA, Shockwave Therapy and Dry Needling, HelloPhysio can help you get back on your feet stronger than before. Contact us to make an appointment today.